Europe is on a mission to become more sustainable, and part of that push includes reducing carbon emissions under the European Green Deal. This ambitious strategy aims to reduce pollution and shift the economy toward cleaner resources. This plan is at the heart of measures targeting better product design, efficient resource usage, and improved recycling practices.
According to the Digital Product Passports: A Blockchain-based Perspective report, one of the European Union’s latest ideas for making this happen is the concept of Digital Product Passports (DPPs).
These passports are designed to promote transparency, encourage the responsible use of resources, and help consumers make more informed choices. In this article, we’ll explore how DPPs work and focus on how NFTs can bring transparency and trust to these digital records.
What are Digital Product Passports?
Digital Product Passports, or DPPs, keep track of everything that happens to a product, starting from the moment its raw materials are extracted all the way through manufacturing, shipping, and even recycling. Think of a DPP as a digital file that follows an item through its entire “life,” storing key information such as ingredients, environmental impacts, and repair opportunities.
This system is part of the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR), which pushes manufacturers to design goods with minimal waste and carbon emissions. Another important driver is the Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP). Both ESPR and CEAP encourage businesses to design products in a way that lets them be reused, repurposed, or recycled—rather than tossed aside.
So, what are the big benefits of DPPs?
- Transparency: They let people see a product’s sustainability details, like its carbon footprint or whether it uses recycled materials.
- Circularity: They highlight how easy a product is to repair or recycle, giving products a longer life and reducing waste.
- Regulatory Compliance: They help companies stay aligned with new EU rules on cutting emissions and managing resources wisely.
Why NFTs?
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, have gained attention mostly for digital art sales. But their usefulness goes beyond collectibles. Essentially, an NFT is a unique digital certificate that lives on a blockchain. No two NFTs are the same, which makes them excellent for proving that a particular item is one-of-a-kind.
In the world of Digital Product Passports, NFTs can act as digital twins. Imagine a one-to-one digital version of a physical product—like a car part, a battery, or a piece of clothing. Once an NFT is connected to that real-world product, it’s incredibly hard to tamper with the history logged on the blockchain.
This characteristic, called immutability, is key. Blockchains store data in a way that’s permanent, so once something is recorded, it’s nearly impossible to modify it without leaving a trace. On top of that, NFTs can update in real-time to reflect changes in ownership, product repairs, or where and how it gets recycled.
NFT Benefits for Digital Product Passports
Verifiable Proof of Provenance
One of the biggest perks of using NFTs for DPPs is being able to trace a product’s origin. The Digital Product Passports: A Blockchain-based Perspective report describes how certain projects create an NFT for each unit of material to confirm exactly where it was mined and how it moved through the supply chain.
Accountability & Trust
Because a blockchain is shared among many computers (a decentralized ledger), the data it holds isn’t controlled by a single authority. This structure helps build trust: everyone with access can see records of who updated what, and when. That transparency reduces the chance of sneaky alterations or fraud.
Secure Ownership & Transfer
In real life, products often change hands. Maybe you sell your phone or give away a handbag. In an NFT-based DPP system, the transfer of ownership can be instantly documented. The NFT’s transaction history can show who owned it before, making secondhand markets more trustworthy.
Hybrid Privacy Approaches
Not everything can live in plain view on a public blockchain—especially sensitive or competitive data. So, some NFT systems use methods like zero-knowledge proofs (a fancy way of proving you know something without revealing the actual data) or selective disclosure (only revealing parts of the data). This ensures sensitive information stays private while still allowing enough transparency to maintain trust.
Real-World Examples of DPPs using Blockchain Tech
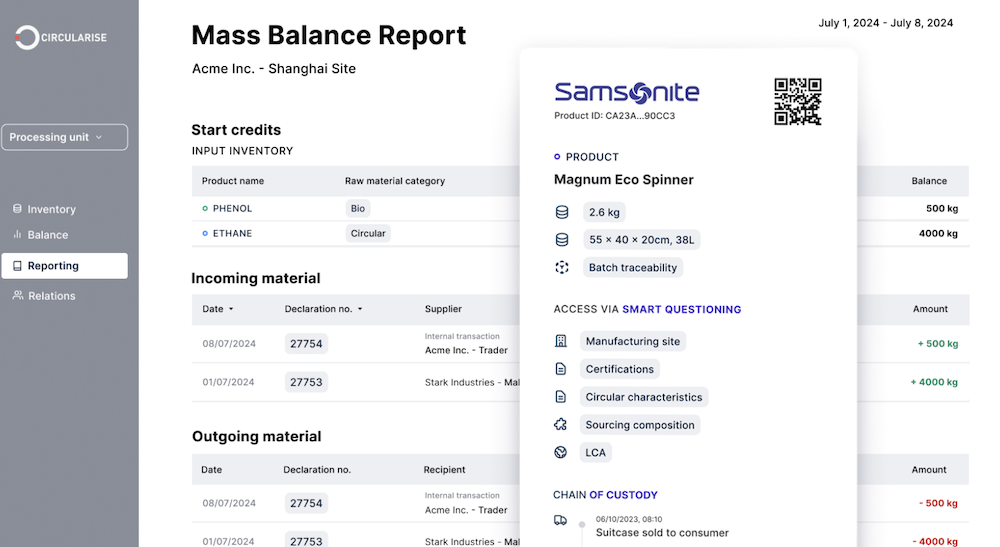
Circularise
- Focus: Builds blockchain-based supply chain solutions that let manufacturers and recyclers see detailed information about materials. Each product or component is assigned a unique token containing real-time data about its material composition and environmental impact. They are working on using NFTs, decentralized identifiers (DIDs), and verifiable credentials (VCs) to enhance the functionality of DPPs.
Other Industry Pilots
- Battery Pass & nChain: These rely on private or permissioned blockchains, where only approved members can add or view data. This can be useful for meeting strict EU battery regulations.
- Spherity emphasises DIDs and verifiable credentials VCs. These tools help verify the identity of whoever’s logging data in the NFT-based passport.
Challenges & Limitations of NFTs for DPPs
Regulatory Acceptance & Interoperability
Some EU rules might require a QR code on every product, which isn’t the same as an NFT. So, companies need to figure out how to align their NFT approach with official regulations. Different blockchain systems must also work together; otherwise, data could become scattered and incompatible.
NFTs vs. Batch-Level Traceability
NFTs are fantastic for tracking individual items, but they have limits when you want to represent batches of identical products or materials. Technically, you can track multiple units with a single NFT, but that risks “double spending” (using the same token to represent more than the actual amount).
Data Privacy Concerns
European privacy laws (like GDPR) restrict how personal or sensitive information is handled. Simply putting everything “on-chain” might conflict with these rules. That’s why many projects are moving to “hybrid” models, storing some data securely off-chain while keeping ownership records on the blockchain.
User Adoption & Market Skepticism
NFTs became famous for digital art speculation, leading some people to think they’re just hype. Educating manufacturers, consumers, and regulators on how NFTs can actually solve real problems is crucial.

Looking Ahead: The Future of NFTs in DPPs
DPPs may soon combine with other cutting-edge ideas—like IoT sensors that send real-time info on a product’s condition, or AI that sifts through data for insights. NFTs could become smarter too, automatically updating when sensors detect changes (say, a battery’s charge level or wear-and-tear on a machine part).
It’s not just about the EU. Other regions might adopt similar rules to monitor raw material sourcing or limit counterfeit goods. That’s why companies embracing NFT-based DPPs now might gain a competitive edge globally.
The future of product transparency looks bright, but also complex. The Digital Product Passports: A Blockchain-based Perspective report highlights how NFTs tackle core challenges in Digital Product Passports—like ensuring authenticity and tracking ownership—while introducing new considerations around data privacy and cost.
Still, NFTs remain a powerful tool for building transparent, trustworthy product histories. Whether tracing ethically mined cobalt or verifying the recycled content in clothing, NFTs allow all parties to see and trust the same set of facts.
Editor’s note: Written with the assistance of AI – Edited and fact-checked by Jason Newey.
Credit: Source link




























